前言
接口统一封装、统一返回可以更规范地给出接口返回的状态码和信息。
实现
状态码封装
这里以常见的状态码为例,包含 responseCode 和 description 两个属性。
如果还有其它业务状态码,也可以放到这个类中。
package com.langjialing.helloworld.config.response;
/**
* @author 郎家岭伯爵
* @time 2023/3/31 14:07
*/
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author pdai
*/
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
public enum ResponseStatus {
SUCCESS("200", "success"),
FAIL("500", "failed"),
HTTP_STATUS_200("200", "ok"),
HTTP_STATUS_400("400", "request error"),
HTTP_STATUS_401("401", "no authentication"),
HTTP_STATUS_403("403", "no authorities"),
HTTP_STATUS_500("500", "server error");
public static final List<ResponseStatus> HTTP_STATUS_ALL = Collections.unmodifiableList(
Arrays.asList(HTTP_STATUS_200, HTTP_STATUS_400, HTTP_STATUS_401, HTTP_STATUS_403, HTTP_STATUS_500
));
/**
* response code
*/
private final String responseCode;
/**
* description.
*/
private final String description;
}
返回内容封装
包含公共的接口返回时间 timestamp,状态 status,消息 message, 以及数据 data。
考虑到数据的序列化(比如在网络上传输),这里 data 有时候还会 extends Serializable。
package com.langjialing.helloworld.config.response;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @author 郎家岭伯爵
* @time 2023/3/31 14:09
*/
@Data
@Builder
public class ResponseResult<T> {
/**
* response timestamp.
*/
private long timestamp;
/**
* response code, 200 -> OK.
*/
private String status;
/**
* response message.
*/
private String message;
/**
* response data.
*/
private T data;
/**
* response success result wrapper.
*
* @param <T> type of data class
* @return response result
*/
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> success() {
return success(null);
}
/**
* response success result wrapper.
*
* @param data response data
* @param <T> type of data class
* @return response result
*/
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> success(T data) {
return ResponseResult.<T>builder().data(data)
.message(ResponseStatus.SUCCESS.getDescription())
.status(ResponseStatus.SUCCESS.getResponseCode())
.timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
}
/**
* response error result wrapper.
*
* @param message error message
* @param <T> type of data class
* @return response result
*/
public static <T extends Serializable> ResponseResult<T> fail(String message) {
return fail(null, message);
}
/**
* response error result wrapper.
*
* @param data response data
* @param message error message
* @param <T> type of data class
* @return response result
*/
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> fail(T data, String message) {
return ResponseResult.<T>builder().data(data)
.message(message)
.status(ResponseStatus.FAIL.getResponseCode())
.timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
}
}
接口返回时调用
在接口返回时调用, 以 user 接口为例:
package com.langjialing.helloworld.controller;
import com.langjialing.helloworld.config.response.ResponseResult;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.map.LRUMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author 郎家岭伯爵
* @time 2023/3/22 9:30
*/
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class UserController {
/**
* 最大容量 100 个,根据 LRU 算法淘汰数据的 Map 集合
*/
private LRUMap<String, Integer> reqCache = new LRUMap<>(100);
@GetMapping("/add")
public ResponseResult<String> addUser(@RequestParam String userId){
// 非空判断(忽略)...
synchronized (this.getClass()) {
// 重复请求判断
if (reqCache.containsKey(userId)) {
// 重复请求
log.info("请勿重复提交:{}", userId);
return ResponseResult.fail("400","执行失败!");
}
// 存储请求 ID
reqCache.put(userId, 1);
}
// 业务代码...
log.info("成功添加用户:{}", userId);
// return "执行成功!";
return ResponseResult.success("执行成功!");
}
}
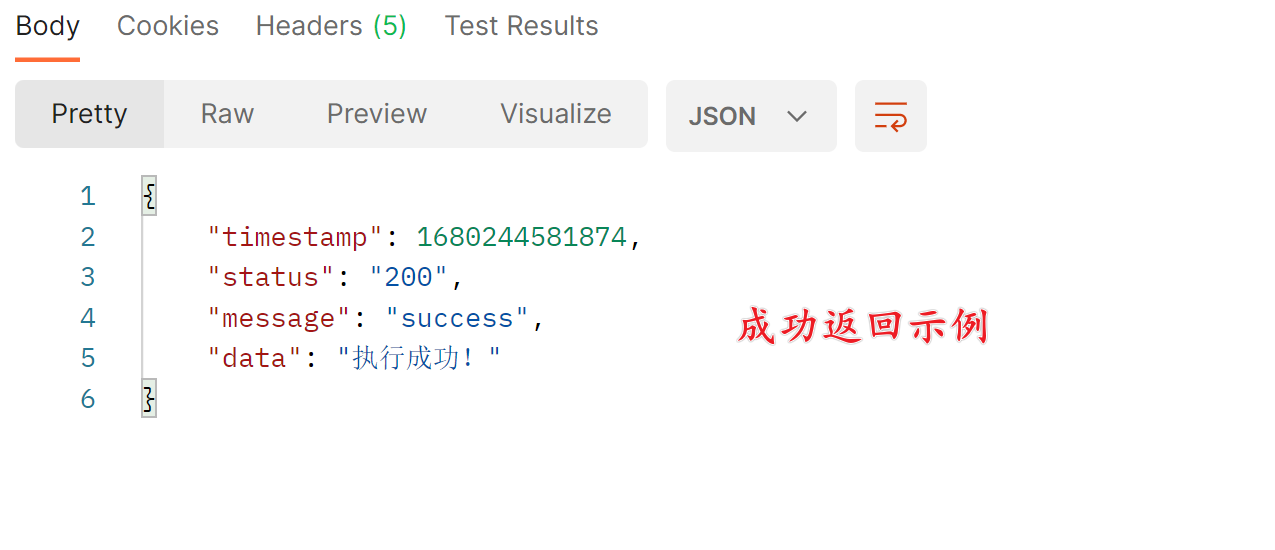
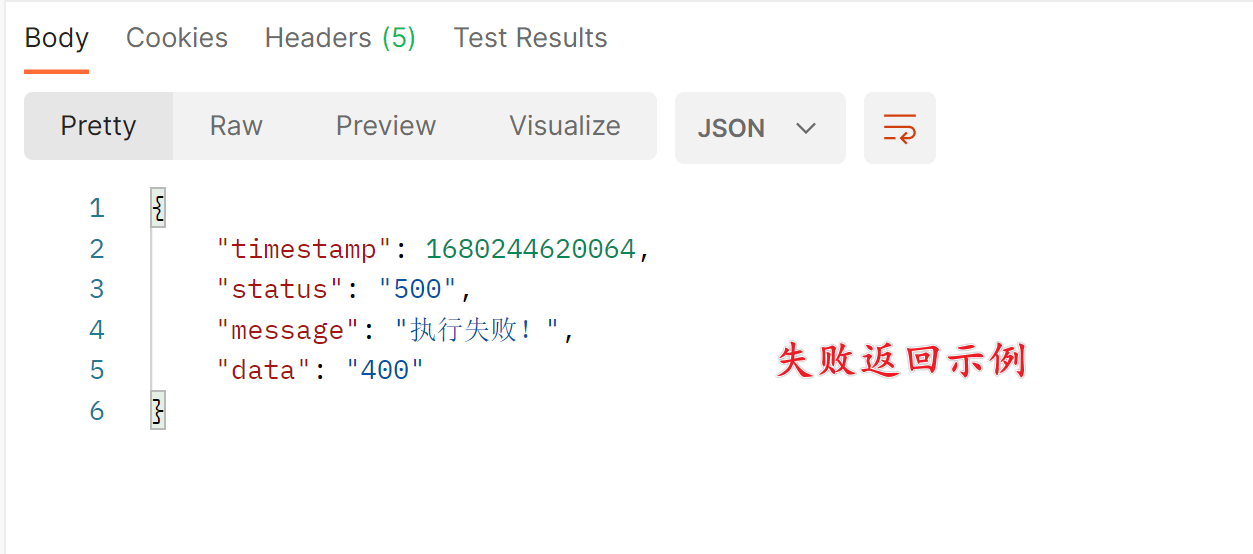
总结
接口统一封装在开发中是一种比较规范的做法,通常来说我们应该在自己的接口或者项目中封装统一的返回状态码和信息。